Create Interactive Lesson
Edit and enhance the pre-generated lesson on Newton Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion
An interactive lesson on the fundamental principles of classical mechanics.
Newton's First Law of Motion states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. This law is often referred to as the law of inertia.
Question 2
Which of Newton's laws states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force?
Discussion
Discuss real-life examples where Newton's First Law of Motion is observed. How does this law explain the importance of seatbelts in vehicles?
Newton's Second Law of Motion describes the relationship between an object's mass and the amount of force needed to accelerate it. The law is often expressed as F = ma, where F is the net force applied, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration.
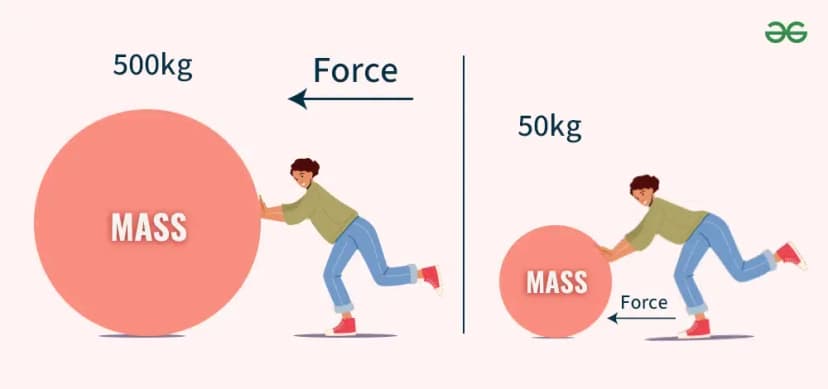
Question 5
Newton's Second Law of Motion states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
Newton's Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects.
.png&w=828&q=75)
Reflection
Reflect on how Newton's Third Law of Motion applies in your daily life. Provide at least two examples and explain your reasoning.